The Gist
As the world becomes increasingly digital and connected, healthcare technology is rapidly evolving to keep up. The digital transformation of healthcare (as tired as we all are of this phrase) is not just a fad but a necessity. It’s the key to improving patient care and driving down costs, as well as improving the efficiency and experience of both patients and providers. There are some key digital health trends (from telehealth to virtual reality and more) that we can expect to shape the future of the healthcare industry.
Keeping track of the rapid changes in healthcare technology is no small task. The industry has seen numerous healthcare technology trends emerge in recent years — some out of convenience and others out of necessity. And with the pandemic still wreaking havoc on the healthcare sector, staying informed about the latest innovations and tech trends is more important than ever.
Healthcare technology will continue to evolve quickly and make a meaningful difference in how healthcare is delivered in the United States. A big part of that is decreasing costs for health systems and hospitals and optimizing how healthcare staff spends their time. Technology will also save doctors valuable time by handling all the information gathering and documentation for them so they can focus on the intelligent part — making decisions and taking the right action based on the given information for every patient. Technology will continue to improve the quality of care for all — step by step.
~ Varun Ganapathi, Chief Technology Officer and Co-founder of AKASA
The task of staying on top of every healthcare technology trend is impossible, as new technologies are emerging every day. But several trends stand out and merit close attention. Here are the top nine healthcare technology trends for healthcare professionals to watch.
1. Telehealth
Prior to the pandemic, telehealth was a rarity. Now, in the wake of the pandemic and lockdowns, virtual care has become one of the most important areas of healthcare technology.
In March 2020, the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) reported a 154% increase in telehealth visits in a single week, compared to the previous year. As telehealth has been pushed to the forefront, policy changes and new rules have been introduced to make digital healthcare services more accessible to all Americans.
In 2021, the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services (HHS) launched an initiative to make telehealth services more affordable through Medicare, allowing beneficiaries to pay less out of pocket. The program also aims to reduce the administrative burden for healthcare providers.
Last February, HHS also announced a $55 million investment in virtual healthcare accessibility, which will open up even more opportunities.
As the pandemic and the public health emergency decelerate, many wonder what will happen to telemedicine.
The Connect for Health Act is a proposed bill that would extend coverage for telehealth services. As of December 2022, it has 68 senate sponsors and is awaiting a vote in the house of representatives. If it passes, telehealth will become a permanent part of Medicare.
What this means for healthcare
Between the increasing popularity of telehealth and efforts to cement it as part of Medicare post-pandemic, telehealth is set to become a mainstay of healthcare. For organizations that aren’t already set up for providing full-time telehealth care as an option, now is a great time to take the necessary steps.
Healthcare providers need to think about any staffing requirements around delivering telehealth, if their online portals are set up to support it and if their current telehealth experience is meeting patient expectations. These steps will lead toward a great telehealth experience, allow organizations to meet patients where they are, and ultimately attract more patients as well.
2. Big Data
Big data is the term used to describe the large volume of information that inundates a business or organization daily. It’s collected from various sources and then processed into insights that help organizations make informed decisions.
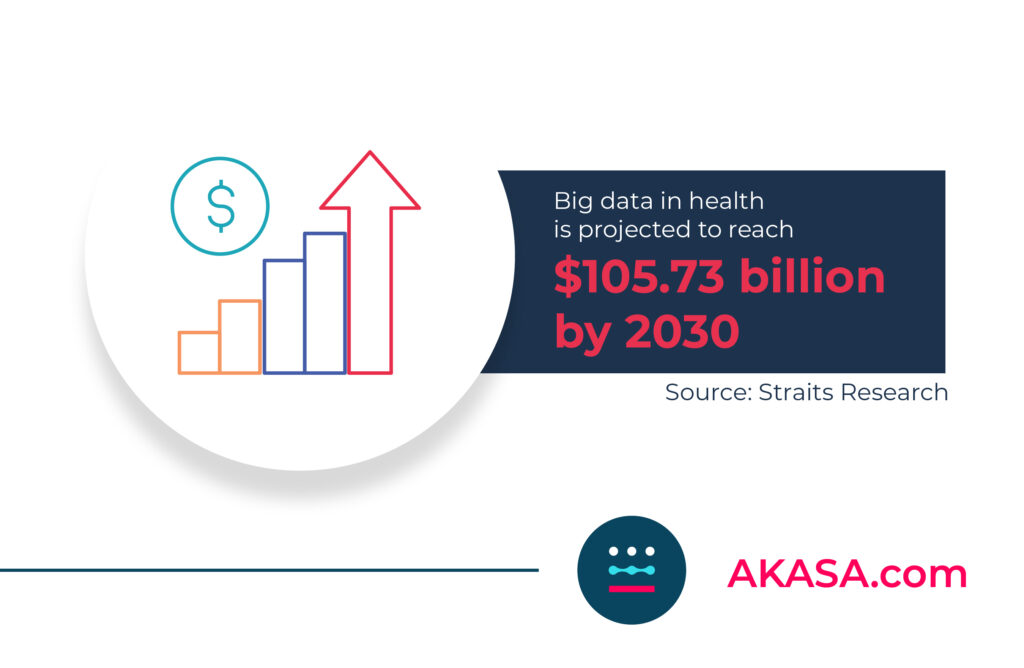
Healthcare is no stranger to big data. Every patient interaction generates a large amount of healthcare data, all of which is stored as electronic health records. All this healthcare data adds up, too — the global big data healthcare market size was valued at $32.9 B in 2021 and is predicted to reach $105.73 B by 2030.
In terms of digital health and using big data, predictive analytics and knowing how to interpret data could be the key to understanding patients better, identifying health risks, and improving health outcomes.
For example, through machine learning algorithms, healthcare workers can identify health risks, plan treatment, and ultimately leverage more informed decision-making around patient care. This potential makes it possible for future platforms to extract big data from patient records, search engines, generic databases, and even social media to get a more complete picture of patients and their overall health.
Of course, this poses an overall risk to public security and privacy. If the patient data is stored and processed by a third party, it’s necessary to have a contract in place with that company to ensure the data is handled in a way that ensures this privacy and minimizes the risk of data breaches. It’s also important for any vendors handling data to abide by HIPAA regulations.
What this means for healthcare
We can expect to see an increase in healthcare organizations implementing blockchain technology for big data and analytics. A blockchain is a decentralized database that stores information in blocks and is secured by a public key. Each block contains a timestamp and a link to the previous block. It can’t be changed once it has been recorded, and only a medical professional with the correct key can access it.
The security behind blockchain makes it an ideal storage system for medical records and other personal information. Attackers would require a huge amount of computing power to infiltrate the network, and there would be no way to change or delete the information. Cybersecurity is always a concern of healthcare systems, and blockchain has the potential to check the right boxes in this regard.
(Read about how AKASA prioritizes data security and privacy.)
It’s also increasingly important that healthcare organizations learn to interpret big data. It’s easy to suffer from data overload. Having staff specialized in data analytics will allow your organization to make the most of all this data, from understanding patient trends to payer habits to RCM optimization and beyond.
3. VR and XR
Virtual reality (VR) and extended reality (XR) are terms used to describe three-dimensional computer-generated environments. VR uses special hardware and software to create the illusion of being present in a simulated environment. XR takes this a step further and allows the user to interact with the virtual environment similar to real life.
In healthcare, VR and XR have the potential to revolutionize the way doctors and patients interact. For example, VR can be used in remote patient monitoring as well as to better understand patients by simulating the experience of dementia, depression, and other mental health conditions. The technology can also aid in rehabilitating people with physical injuries. Training doctors in performing surgeries and other medical procedures is also a possibility.
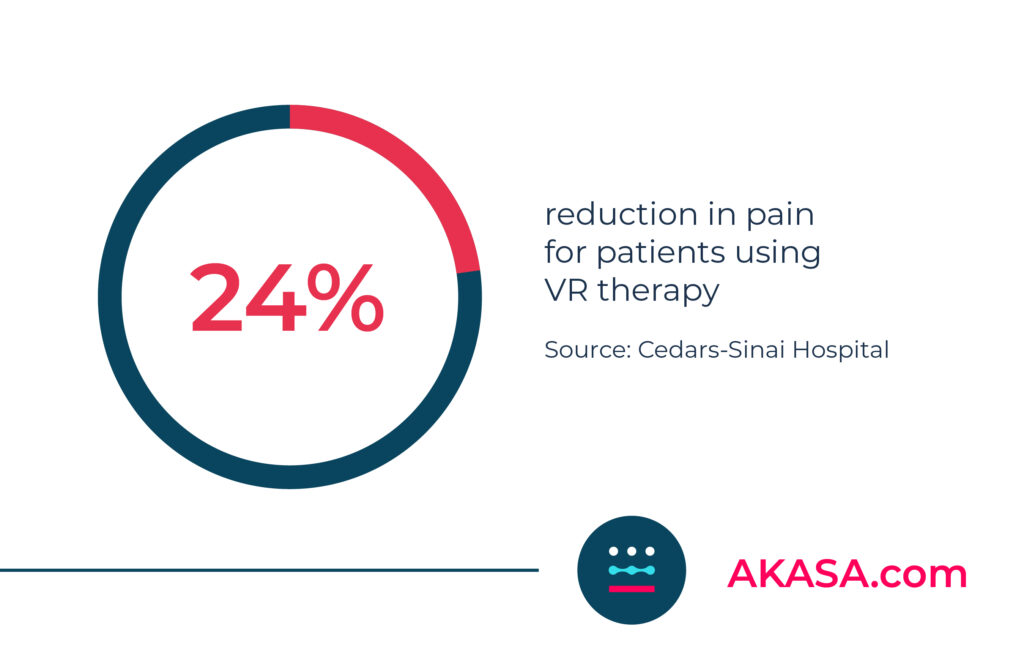
Healthcare systems are seeing a surge in the number of patients using VR to improve their healthcare experience. Cedars-Sinai Hospital in Los Angeles has reported that VR could reduce the amount of pain patients experience by 24% or more.
What this means for healthcare
In the coming year, expect more hospitals and medical centers to implement VR and XR in their healthcare programs. The applications of VR and XR in healthcare are only beginning to be discovered, and the potential benefits are too great to ignore.
For healthcare providers without the staff or financial resources to pursue VR and XR at the moment, 2023 is still a great opportunity to see how other providers utilize the technology.
4. Artificial Intelligence
Artificial intelligence (AI) isn’t a new concept, but it’s experiencing significant growth. In healthcare, AI has been used to help doctors diagnose and treat their patients. But AI in healthcare is seeing rapid advancement.
There are many AI-based health technologies currently being used in the healthcare industry. Some of the more well-known include IBM Watson, Google DeepMind, and Apple HealthKit. However, many other AI-based healthcare applications are being developed.
For example, a company called Sense.ly has developed a virtual nurse app that uses AI and machine learning (ML) to communicate with patients and providers, responding to questions with answers from reputable sources. This advanced chatbot integrates its code into health systems and provides real-time information to the medical team from in-depth insights on user behavior and other metrics.
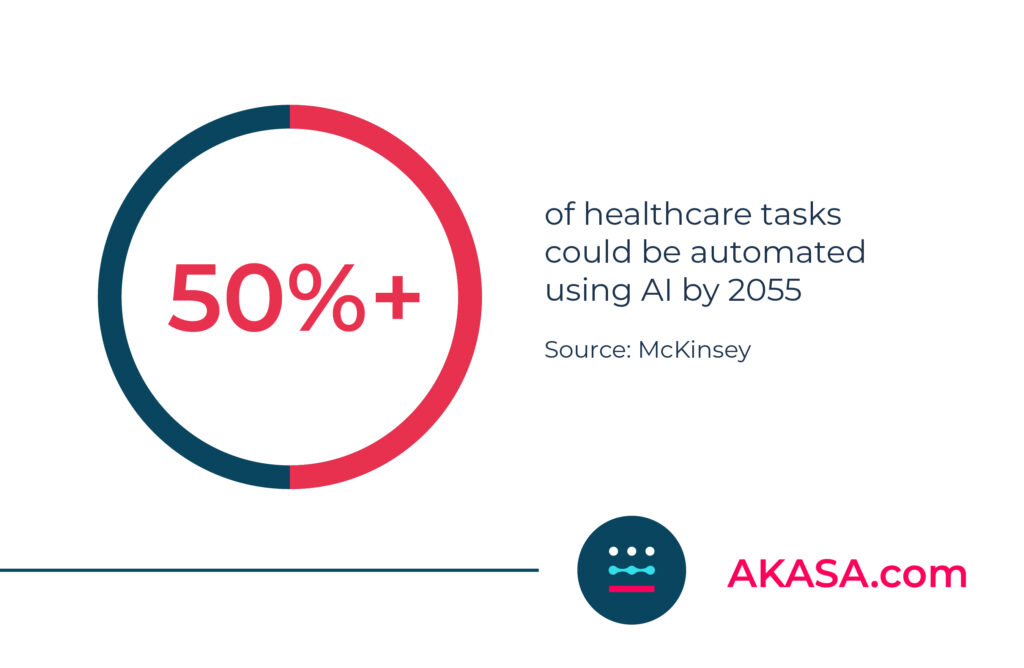
McKinsey predicts that AI, ML, and automation will take over half of all tasks currently done by humans in the healthcare industry by 2055. By that year, healthcare will be dramatically different, and providers will need to approach their services in a whole new way.
It’s exciting to see the rapid progress being made in AI to solve some of the most complex problems in healthcare, including clinician burnout and administrative headaches. As the AI community makes further progress in areas such as ML, natural language processing (NLP), and computer vision, I think we’ll soon be able to predict — automatically — the notes and documentation a doctor might write for a given diagnosis or treatment. This would be a huge achievement! It could save frontline healthcare workers valuable time that could instead be directed to patient care.
~ Varun Ganapathi, Chief Technology Officer and Co-founder of AKASA
What this means for healthcare
Healthcare AI is changing how many providers deliver care, from using chatbots to triage patients to making more informed decisions around care. Providers can expect to see even more focus on AI tools as both support and digital teammates in healthcare.
As a result, healthcare organizations need to ensure their teams are knowledgeable on the latest AI tools they’re using, and have the right level of technical prowess to use such tools. This could mean bringing in a training consultancy or having in-house experts educate others.
5. Automation
There is still a lot of tedious paperwork healthcare staff needs to do. In the next year, AI and ML will continue to play a big role in automating these manual administrative tasks so staff can spend more time with patients.
~ Varun Ganapathi, Chief Technology Officer and Co-founder of AKASA
Automation is handling more and more tasks that care providers and healthcare staff performed daily in the past. It has numerous applications in healthcare, from simple automated text reminders of appointments to more advanced uses like automatic alerts of potential drug interactions.
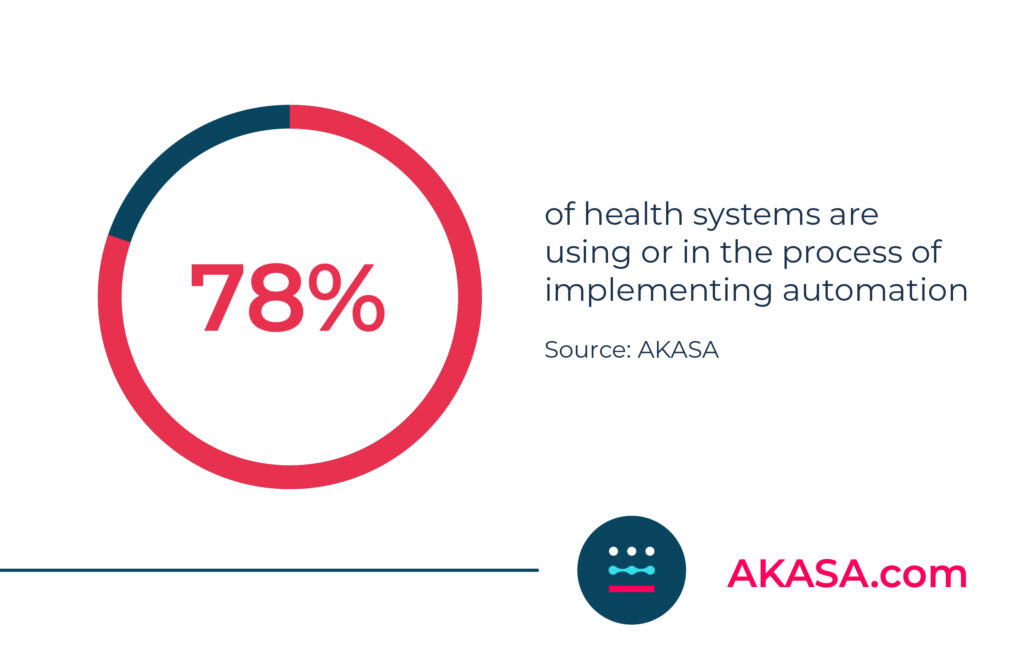
Automation is also frequently used in healthcare revenue cycle management (RCM), where it streamlines the billing process for employees and patients alike. According to an AKASA survey of healthcare leaders, 78% of health systems are using or in the process of implementing automation.
For example, the automation AKASA delivers takes time-consuming healthcare revenue cycle tasks, like claim status and prior authorization, out of the picture. By leveraging the latest in AI and ML, our technology grows in capability and efficiency with every task it completes. Automating these tasks allows provider staff to focus on more important duties, like improving the patient experience and handling more complex and value-generating activities. Organizations are increasing revenue outcomes and doing more with the teams they have.
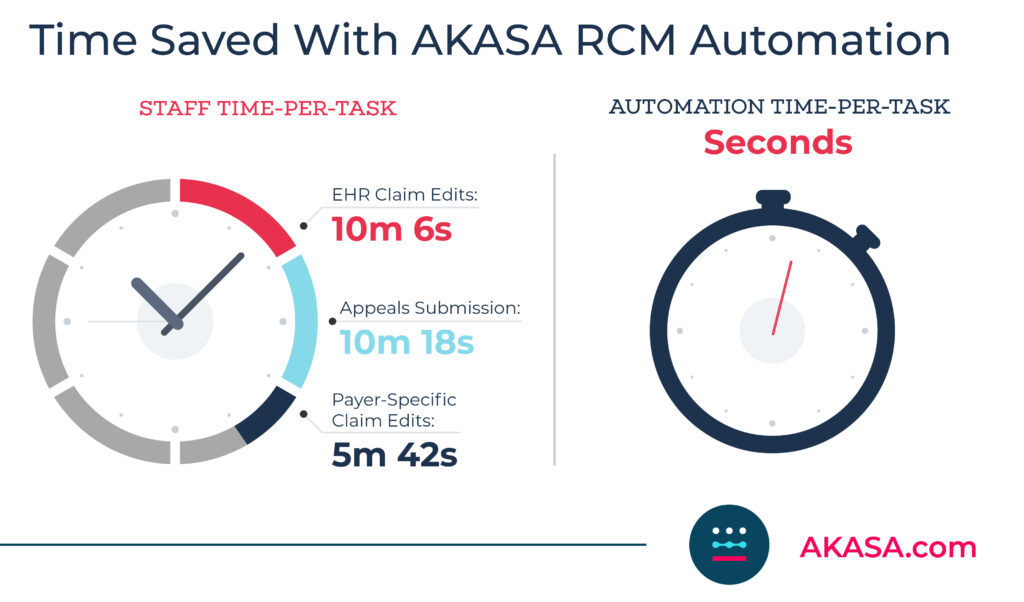
What this means for healthcare
Healthcare automation is already reshaping how certain functions and departments operate. Again, take our automation for example. It’s reshaping the roles of healthcare RCM staff, allowing them to focus on more complex tasks and the patient experience. This makes their roles more interesting, improving engagment and retention.
Check out this ebook on 9 Ways to Engage Your RCM Team.
As automation continues to expand into other avenues of healthcare, both providers and those in healthcare operations will see their roles change. Expect to see an increasing focus on understanding health data and analytics, the use of health tech to better-serve patients, and more.
6. Internet of Medical Things (IoMT)
You may have heard of the Internet of Things (IoT), which is a network of physical devices such as sensors and actuators that collect and exchange data using software and connectivity through cloud computing. The IoMT is a similar concept, but with medical devices.
The IoMT is being used to help healthcare providers monitor and improve patient care. It can also track patient progress, improve hospital operations, and more.
Traditional medical devices and technology are now becoming smart and connected. X-ray and MRI machines, blood pressure monitors, and more are now connected to the IoMT and can be accessed and controlled by caregivers and other medical professionals anywhere in the world.
IoMT can be used to connect patients to their doctors. Patients can use a smartphone or tablet to send medical data to their doctor, who can monitor their progress and be alerted if any changes occur. IoMT can also be used to monitor patients who are at risk for a particular condition. For example, if a patient is in a high-risk group for diabetes, the IoMT can be leveraged to monitor their glucose levels and alert their doctor if they become abnormal.
What this means for healthcare
There are many untapped benefits of the IoMT, but an emerging issue is the security of the data that’s being collected and stored. Modern medical devices as ubiquitous as an MRI machine or heart rate monitor can connect to the IoMT and transmit data, many of which aren’t properly protected.
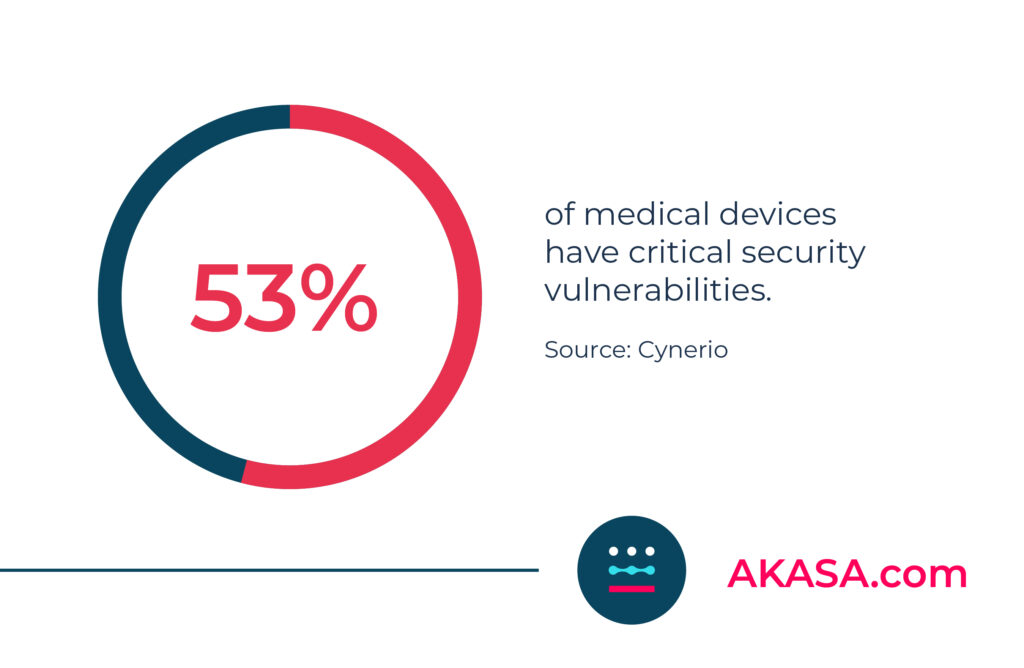
As software development and health tech become more advanced and intertwined, data encryption and security will become even more important than they already are. Healthcare organizations can prepare by auditing their own cybersecurity, ensuring they meet HIPAA standards and have proper action plans in place in the event of a breach.
7. Digital Twins and Simulations
Digital twins are 3D computer models of physical systems or digital replicas of a real object or process. In the medical field, digital twins are used to replicate functions and illnesses, like the function of a heart or even a tumor. Instead of needing to practice a surgical procedure, surgeons can now perform virtual simulations on a digital twin of the patient. Surgeons are even using digital twins to determine optimal treatment for injuries like spinal fractures.
For example, researchers in the European Union are attempting to replicate the human brain using digital twin technology with its Neurotwin project. This project could help develop new and better treatments for neurological diseases, without the need for costly, high-risk human trials early on.
What this means for healthcare
In 2023 and beyond, the technology behind digital twins is poised to advance even further and likely become more commonplace. It’s already become a non-option in a variety of other industries, including manufacturing and design, where it’s regularly used for design and quality testing.
There’s a load of untapped potential with digital twin technology. As this technology becomes more advanced and available, the public could even find uses for it. Imagine using a digital twin to predict the future of your health and then apply changes to your own life to avoid or prevent health problems before they happen.
8. Wearables
Wearable technology, like popular fitness trackers and smartwatches, allows for collecting and monitoring health metrics. Trackable health metrics include heart rate, step count, oxygen levels, and even stress. While wearable technology isn’t new, it’s become more accessible and affordable in recent years.
As wearable technology continues to become more affordable and widespread, the potential for use in the medical field grows.
For example, medical providers could incorporate wearables into their patient intake process. This would allow them to better understand their patient’s overall health, both before and after their appointment. This would also enable even more in-depth long-term care plans for patients, especially those with certain health conditions or goals.
What this means for healthcare
While healthcare organizations aren’t expected to implement wearables into treatment in 2023, the capabilities are already there. For organizations with the resources, beginning to incorporate wearables into treatment and patient data collection will allow their organization to stand out and better serve patients.
The increasing use of wearables in healthcare will also make it especially important that health systems have modern patient portals and systems in place. Without integrated, modern systems, collecting patient data through wearables will be difficult and ineffective.
9. Smart Implants
Smart implants are medical implants with technological capabilities. They serve their core medical function while also enabling additional functionality, like health monitoring and data transmission.
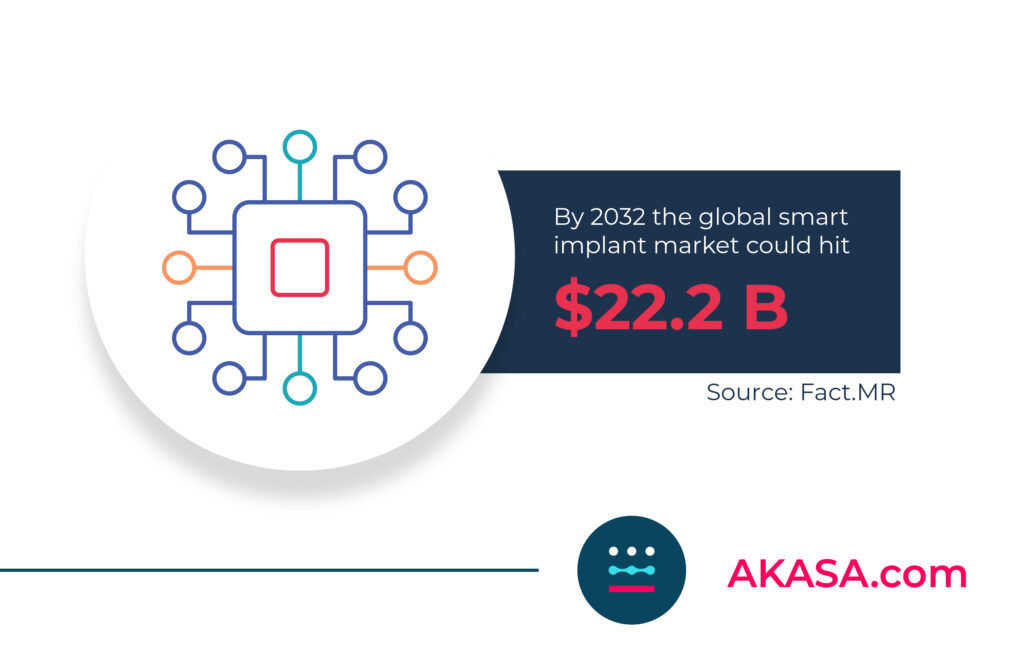
Smart implants may sound like something out of science fiction, but the global market for smart implants is already valued at $3.9 billion and could hit $22.2 billion by 2032. And there are a number of FDA-approved smart implants currently in use today.
Zimmer Biomet and Canary Medical’s smart knee implant, called Persona IQ, allows doctors to track the post-operative recovery process for a patient through objective data collection. The device is implanted into the knee and collects data on the patient’s range of motion and joint function. It then sends that information to a cloud service where doctors and clinicians can review the data for up to 10 years.
This is only one of many examples of medical professionals currently using smart implants. Much like wearable devices, smart implants will likely see an uptick in popularity and use as they become increasingly smaller and more affordable.
What this means for healthcare
Much like wearables, smart implants will make it especially important that healthcare organizations have modern patient systems and proper interoperability in place. Smart implants are only smart if they can communicate with the provider’s portals and transmit the various metrics and data points.
Even if a healthcare provider isn’t planning on using smart implants in 2023, it’s never a bad idea to audit and modernize any patient systems lagging behind.
Healthcare Today and Beyond
Healthcare technology is allowing for unprecedented levels of care, improving patient outcomes, and helping organizations keep up during a time of staffing challenges.
For example, AI-powered automation from AKASA makes end-to-end RCM automation possible. This allows revenue cycle teams to keep up with the increasingly complex billing process, improve billing accuracy, and better serve their communities.
You can’t predict the future, but you can prepare for it. Future-proof your healthcare RCM efforts with AKASA today. Request a demo of the AKASA platform.











